Sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis
Two significant lung diseases that require assessment include sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis. The most typical type of interstitial pneumonia is pulmonary fibrosis, a respiratory disorder. This description refers to the process by which altered connective tissue, which is stiff and fibrous, eventually substitutes normal pulmonary tissue by invading the elastic lung tissue.
The lungs and lymph nodes are the primary organs affected by the inflammatory disease sarcoidosis, which can also affect other organs. Sarcoidosis is covered in this manual. To learn more about the causes, signs, and treatments for sarcoidosis and fibrosis, read this section carefully.
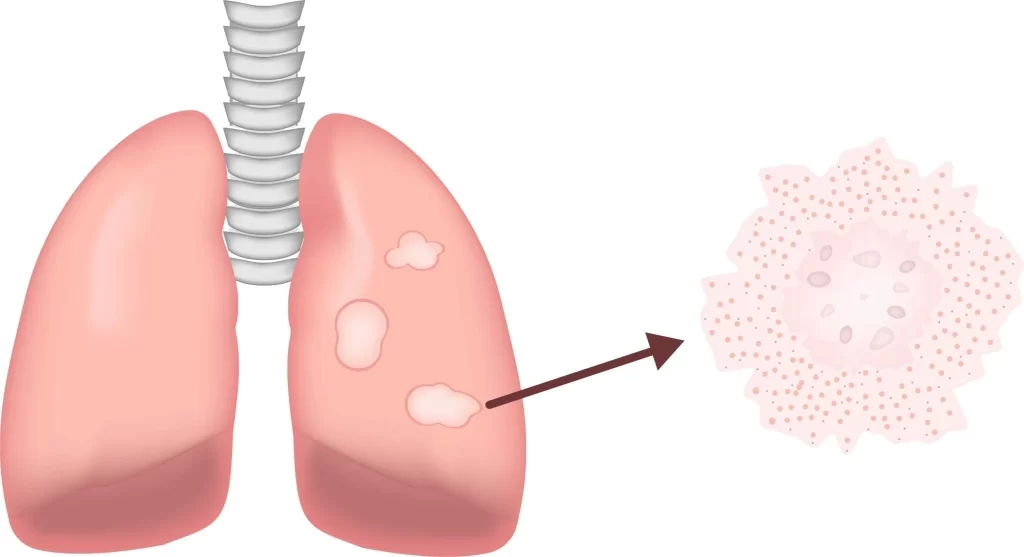
What is pulmonary fibrosis?
Respiratory distress is brought on by pulmonary fibrosis, which prevents these organs from exchanging oxygen for carbon dioxide. Respiratory failure, secondary pulmonary hypertension, right-side heart failure, and an elevated risk of pulmonary cancer are all potential complications of this illness. Pulmonary fibrosis is irreversible; however, treatments can delay the progression of the disease, decrease manifestations, and enhance the quality of life.
What are the contributing factors of pulmonary fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis can be caused by encountering airborne pollutants, including silicon dust and asbestos fibers, as well as radiation therapy, chemotherapy, antiarrhythmics, and certain antibiotics. On the other hand, rheumatological diseases like connective tissue disease, particularly systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, rheumatoid arthritis, and sarcoidosis, can also be linked to pulmonary fibrosis. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is the term used when it is impossible to determine the cause of the stimulant.
What are the pulmonary fibrosis symptoms?
Breathing difficulties, fatigue, dry coughs, and all other symptoms associated with underlying diseases are the main signs and symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis. The rate and speed of progression of symptoms vary widely from case to case.
Diagnosis
Clinical visits and tests are as follows:
- Alveolar-capillary diffusion of carbon monoxide and spirometry
- High-resolution lung-specific CT scan
- Blood gas testing
- Eco cardiography
Pulmonary fibrosis treatment
Currently, no medication has the ability to slow or stop the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Nevertheless, some medications can at least momentarily reduce symptoms while also delaying the disease’s progression.
The medications corticosteroids and N-acetylcysteine are employed to treat pulmonary fibrosis. Additionally, prescribed medications include immune system suppressants, including cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil. In cases of hypoxemia, oxygen therapy might help to improve breathing. It might be given in circadian rhythm or just when someone is resting or exercising. The quality of life is enhanced by cardiopulmonary rehabilitation.
What is sarcoidosis?
Granulomas, aberrant nodules comprised of inflammatory tissue, are a hallmark of the disease sarcoidosis. Depending on the organs involved and the level of inflammation, it can occur in a variety of ways and to varying intensities. Children and the elderly are rarely affected by sarcoidosis, which primarily affects adults.
What factors lead to sarcoidosis?
Sarcoidosis still has no identified etiology. The dysfunction of the immune system that causes granulomas to form in many body organs is recognized to be connected to this disease. Investigations are still ongoing to determine what triggers stimulate this inflammatory reaction.
Genetics has been suggested (though not yet confirmed) to play a role in the causation of the disease because some populations are more affected than others (for example, African-Americans).
What are the symptoms of sarcoidosis?
Depending on whatever organ is impacted, sarcoidosis symptoms can differ. We will experience the following symptoms in the lung, one of the organs most negatively impacted by this pathology:
- Dry cough
- Decreased exercise tolerance
- Dyspnea
Enlarged and palpable lymph nodes in the neck, beneath the chin, above the collarbone, in the armpit, and the groin area indicate lymph node involvement, which is prevalent in the disorder.
Also prevalent are dermal manifestations characterized by red or prominent areas, as well as inflamed, painful joints. There may also be non-specific symptoms like a lingering low-grade fever and weight loss.
Sarcoidosis treatment
Sarcoidosis, in the majority of instances, does not necessitate therapy because it disappears within a few months or years. Your doctor may advise making minor lifestyle adjustments and using painkillers (e.g., paracetamol or ibuprofen) to relieve pain. If the disease is not treated with medicine, doctors will periodically order x-rays, breath tests, and blood tests to determine whether it is getting better or getting worse. If it worsens, they might prescribe medication.
-

problems of patients and the medical community
27 خرداد 1402 -
Lung clinic
8 خرداد 1402 -

Long COVID
8 خرداد 1402 -
Sarcoidosis Clinic
8 خرداد 1402 -
?What is lung cancer, and how is it treated
8 خرداد 1402 -

Sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis
8 خرداد 1402 -
What exactly is foreign body aspiration?
8 خرداد 1402 -

How are pulmonary function tests؟
8 خرداد 1402 -

Everything you require to know about the polysomnography
8 خرداد 1402 -
?How is pulmonary rehabilitation carried out
8 خرداد 1402





