Pleuroscopy and thoracoscopy
The pleural membrane, also called the pleura, is the membrane covering the lungs and consists of two layers called the pleural plates. These plates include the parietal and the visceral pleura, the former separating the lungs from the chest wall and the latter covering the inner surface of the lungs. These membranes would have to be examined in case a lung disease occurs in this area. Pleuroscopy and thoracoscopy are the two conventional ways to examine the pleura membrane. The present article introduces these two examination methods. Stay with us.
What is Pleuroscopy?
Pleuroscopy is a medical method used to examine the pleural cavity. The pleura is the space between two layers of tissue covering the lungs.
How is Pleuroscopy performed?
A tube called the pleuroscope is inserted into the pleural cavity through a small incision in the chest wall to perform Pleuroscopy. The doctor can then observe the pleural cavity through the special camera. Pleuroscopy is a relatively non-invasive method of drug injection into the pleural space for patients with effusion (fluid accumulation in the pleural space).
What are the applications of Pleuroscopy?
This technique is generally performed for pleural biopsy and complements previous pleural liquid analysis. The liquid forming in the pleural cavity due to pleural inflammation determines the pleural lesion’s nature precisely.
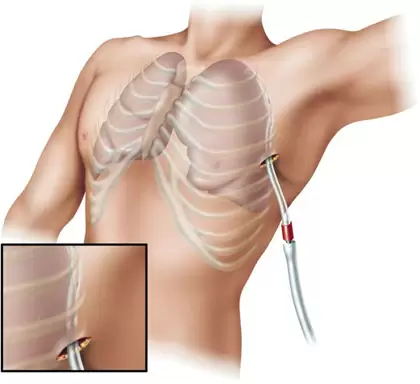
What is thoracoscopy?
Thoracoscopy is a procedure through which an endoscopic instrument is inserted into the pleural cavity and is used for the following purposes:
- Viewing the cavity (pleuroscopy)
- Performing an operation
Partial sedation may be performed for pleuroscopy, and the operation is performed in an endoscopy room under a pulmonologist’s supervision.
Both video thoracoscopy and pleuroscopy involve thoracoscope introduction through a dermal incision and both allow cameras to be used and instruments to be placed. Thoracoscopy would generally require the application of a drain for the next one to two days following surgery.
Thoracoscopy is used in the following cases:
- To investigate pulmonary or pleural lesions and effusions in the case of inconclusive noninvasive tests
- For pleurodesis in patients with recurrent malignant effusions
- For better diagnostic accuracy in pleural tuberculosis disease and neoplastic pathologies
Thoracoscopic surgery consists of the following:
- Correcting the primary spontaneous pneumothorax
- Lobectomy and lung volume reduction surgery in emphysema
- Removing the wedge
- Lung parenchyma biopsy
- Lobectomy and pneumonectomy
Preparing for thoracoscopy
The physician may ask for blood or other routine tests before a thoracoscopy. The patient must disclose the use of any drugs to know whether to cease consumption.
How is thoracoscopy performed?
General anesthesia is administered right before the surgery. Small incisions are then made in the chest, through which the surgeon enters an endoscope and surgical instruments. The optical device includes a small camera transmitting images to the monitor. One or several tubes can be placed in the chest temporarily following the surgery to drain air and fluid. Sutures or stables are used to close the incision.
Post-surgery
Hospitalization may take one to four days. However, the patient will not be discharged until the tubes inserted to drain air and fluids are removed. The patient may feel numb and receive intravenous medication and fluids. Their heart and respiratory rates will be constantly monitored and checked. A physiotherapist will deliver breathing exercises to prevent inflammation, which the patient must perform almost every hour. This also helps the patient move and walk as fast as possible to speed up recovery and improve blood circulation.
-

problems of patients and the medical community
27 خرداد 1402 -
Lung clinic
8 خرداد 1402 -

Long COVID
8 خرداد 1402 -
Sarcoidosis Clinic
8 خرداد 1402 -
?What is lung cancer, and how is it treated
8 خرداد 1402 -
Sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis
8 خرداد 1402 -
What exactly is foreign body aspiration?
8 خرداد 1402 -

How are pulmonary function tests؟
8 خرداد 1402 -

Everything you require to know about the polysomnography
8 خرداد 1402 -
?How is pulmonary rehabilitation carried out
8 خرداد 1402





