?What is lung cancer, and how is it treated
Mutations in cells that are found on the lungs or bronchi induce lung cancer, a group of malignant tumors. Although the right lung is more severely affected than the left by the disease, the upper lobes are also impacted.
This disease progresses slowly over the course of several years. The tumor can spread to other body organs and tissues and is frequently not just restricted to the lungs.
The most prevalent and dangerous type of cancer is, on the other hand, lung cancer. It ranks first in negative consequences and second in terms of prevalence after skin cancer. As a result, knowledge of the causes, locations, symptoms, diagnostic techniques, and therapeutic strategies for tumors is crucial.
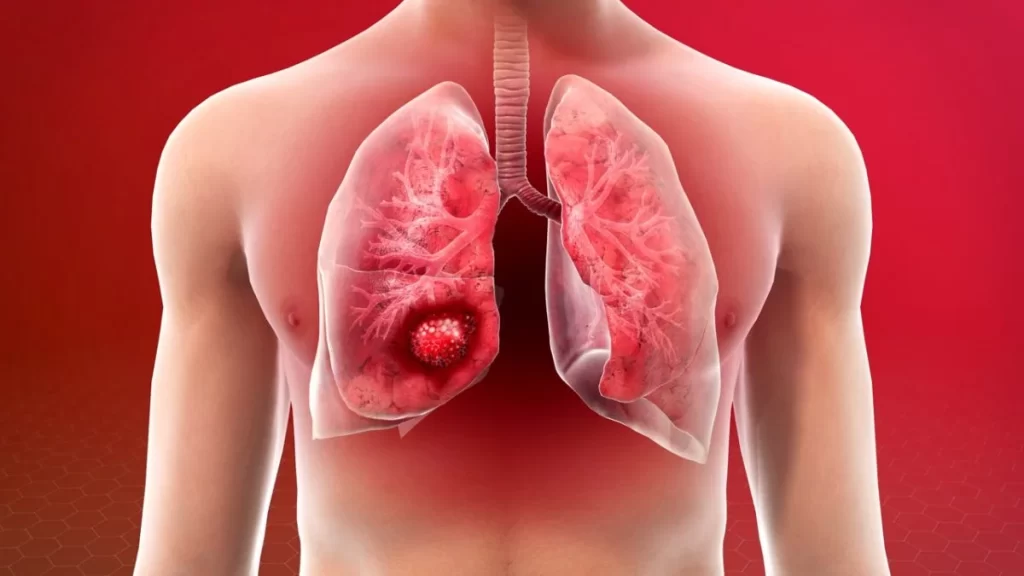
Risk factors for lung cancer
Smoking is the leading factor in 8 out of 10 occurrences of lung cancer; however, non-smokers can also get the disease. The following are some factors that could lead to lung cancer:
- Genetic predisposition
- Regular exposure to volatile carcinogens
- Excessive chest radiation
- Genetic disorders
- Some viruses
- Alcohol abuse and malnutrition
Those with a higher risk of developing this kind of cancer include:
- Smokers older than 40
- Alcoholics
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients
- Individuals with a history of the upper respiratory tract and pulmonary oncological diseases
- Individuals with a family predisposition
- Individuals who are frequently exposed to dust, radon, asbestos
- Individuals with low social standing
- Age over 50, endocrine abnormalities, and chronic lung diseases are examples of individual-independent factors.
How is lung cancer manifested?
Wheezing and a hoarse voice are the disease’s hallmark symptoms. The location of the cancer will also affect the symptoms. Given that the tumor does not impact the nerve terminations, peripheral lung cancer is asymptomatic and painless for an extended period, whereas central lung cancer manifests itself in its initial stages as a cough with sputum combined with blood and pus, continuing dyspnea, sound changes, and general fatigue.
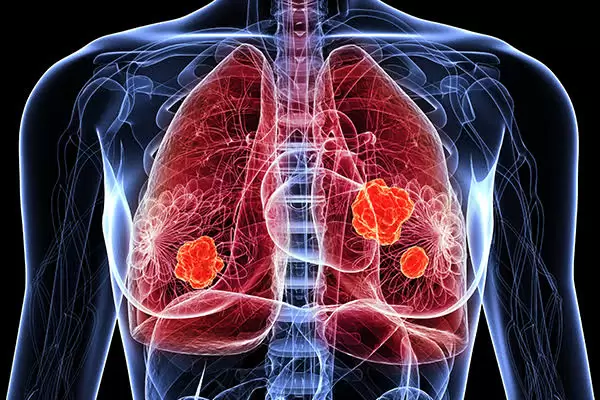
Lung cancer diagnosis
The following are used to diagnose it:
- Radiography (preventive fluorography can identify a number of tumors).
- MRI and CT
- Bronchoscopy of the trachea and bronchi up to the sixth and seventh orders, including with biopsy sampling for histological analysis.
- PET-CT – to evaluate the frequency of metastases and monitor therapeutic efficiency
- Endoscopic or intrabronchial ultrasonography – to evaluate the lymph nodes’ health and the process’ stage
The pulmonary bronchus’ electromagnetic sound enables the early diagnosis of deep neoplasms.
- Thoracoscopy: a video camera is employed to examine the patient through a thoracic hole.
- Blood tests using molecular genetics to identify specific tumor markers
Lung cancer treatment
For lung cancer to be effectively treated, early detection is crucial. In this instance, it is feasible to completely recover and resume regular life after the removal of cancerous tissue
Surgery
A part or the entire lung may be removed if non-germination to other organs and lymph node lesions occur during the procedure. Patients with the first or second stages of the tumor, and to some extent those with the third stage, are candidates for surgical treatment. The surgery is not possible due to the pathology spreading to other vital organs or the patient’s overall serious condition.
Radiology or radiation therapy
In addition to surgery, chemotherapy, and other treatments, guided ionizing radiation—which kills cancerous cells—is employed at all stages. To avoid recurrence or to treat the inoperable condition, radiation therapy is used to treat the tumor non-surgically, eliminate any remaining cells and metastases following surgery, and eradicate the tumor.
Chemotherapy
Before and after surgery, as well as in circumstances where surgery is clinically inoperable, radiation therapy is recommended together with drugs eradicating tumor cells.
Targeted therapy
Contemporary targeted medications are used to prevent the proliferation of well-defined cell types. Targeted therapies lengthen the lives of people with inoperable lung cancer by preventing tumor development rather than removing the tumor. This reduces lung cancer symptoms in both men and women. Rehabilitation of lung cancer patients
Patients’ recovery after surgery to eliminate a portion of the lung encompasses the following:
- Medical gymnastics
- Diaphragmatic breathing training
- Corrective drug treatment
- Respiratory health
- Bronchial drainage to remove fluids
-

problems of patients and the medical community
27 خرداد 1402 -
Lung clinic
8 خرداد 1402 -

Long COVID
8 خرداد 1402 -
Sarcoidosis Clinic
8 خرداد 1402 -

?What is lung cancer, and how is it treated
8 خرداد 1402 -
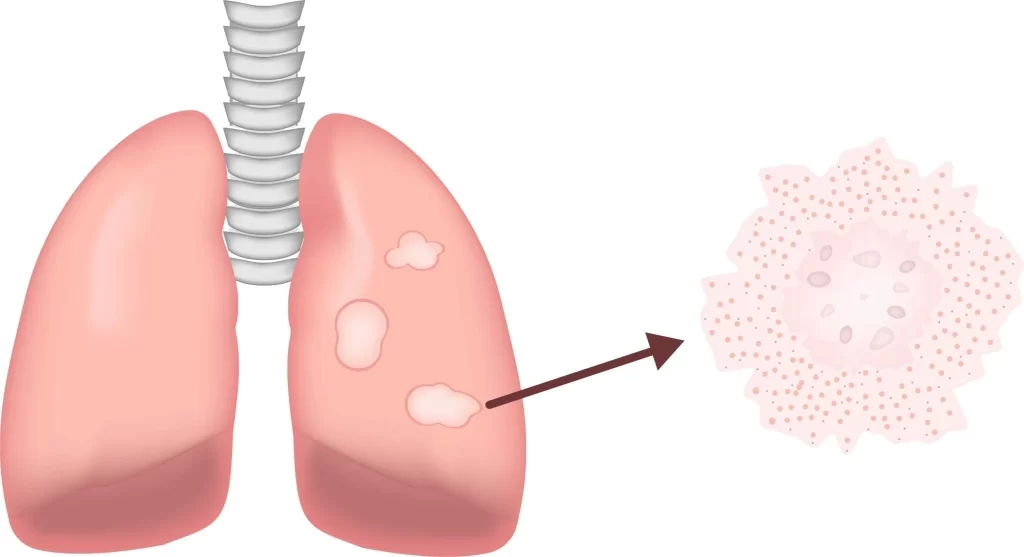
Sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis
8 خرداد 1402 -
What exactly is foreign body aspiration?
8 خرداد 1402 -

How are pulmonary function tests؟
8 خرداد 1402 -

Everything you require to know about the polysomnography
8 خرداد 1402 -
?How is pulmonary rehabilitation carried out
8 خرداد 1402





